Trade in Services drops 7.5% in 2022
 Trade in Services 2022
Trade in Services 2022
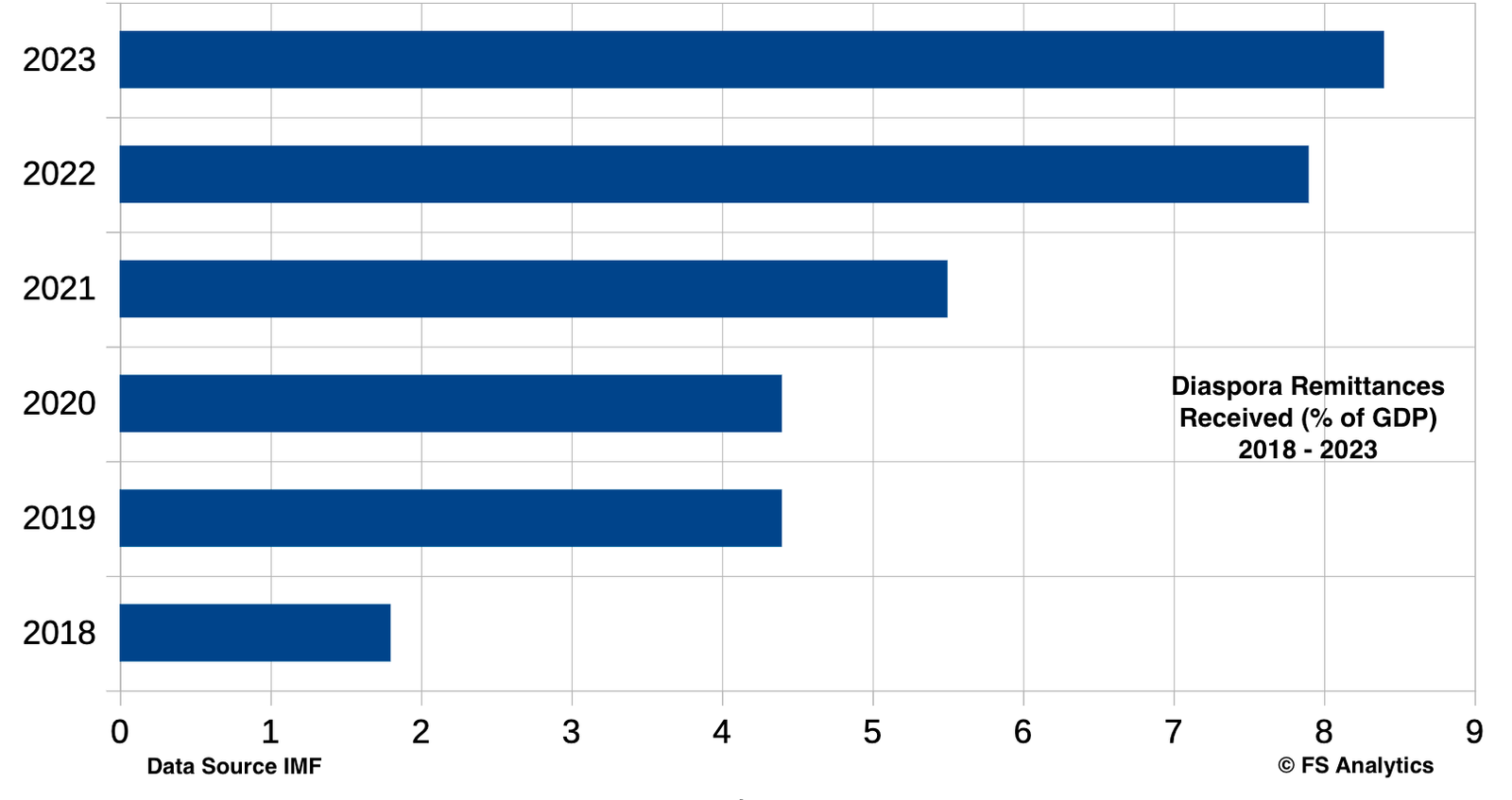
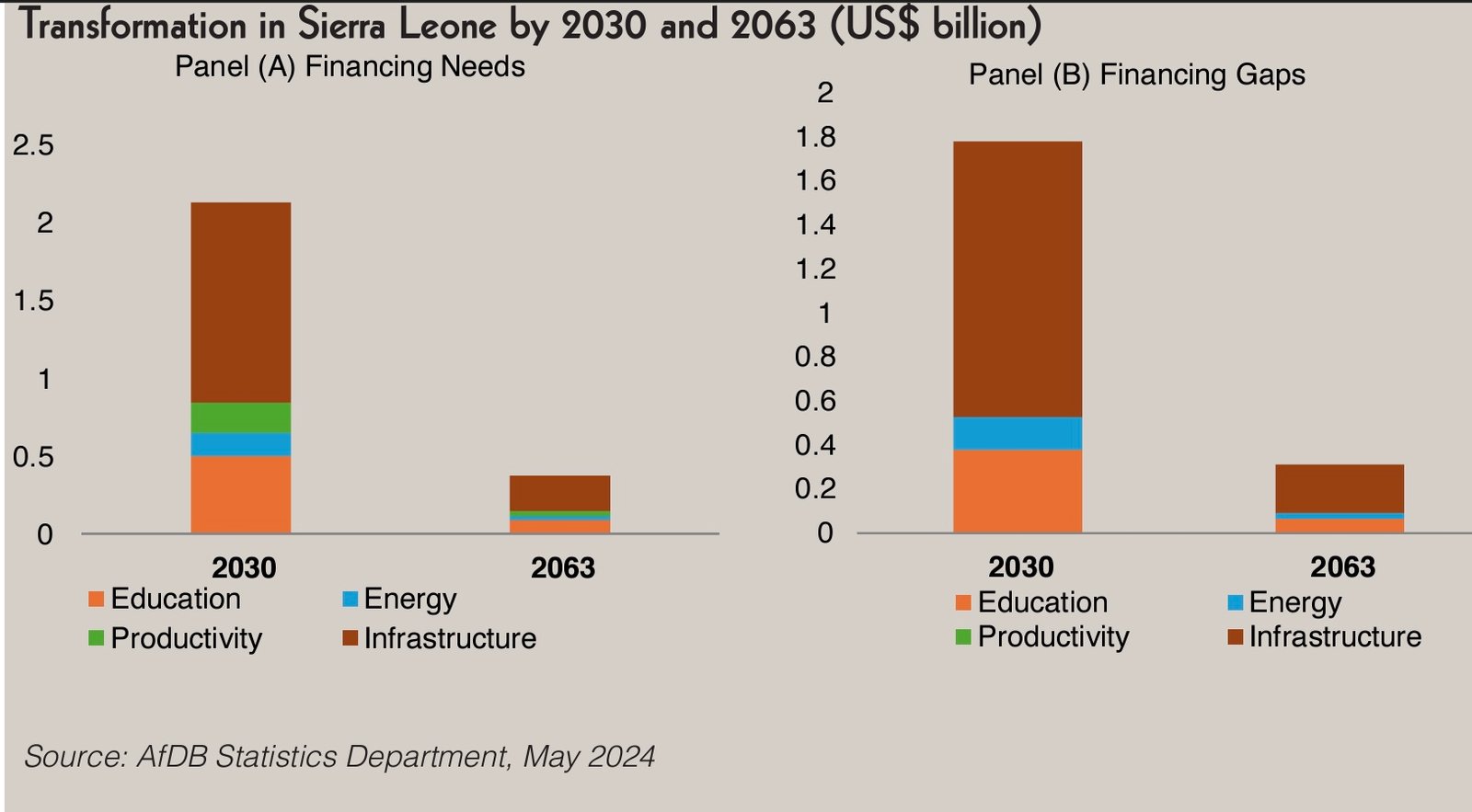
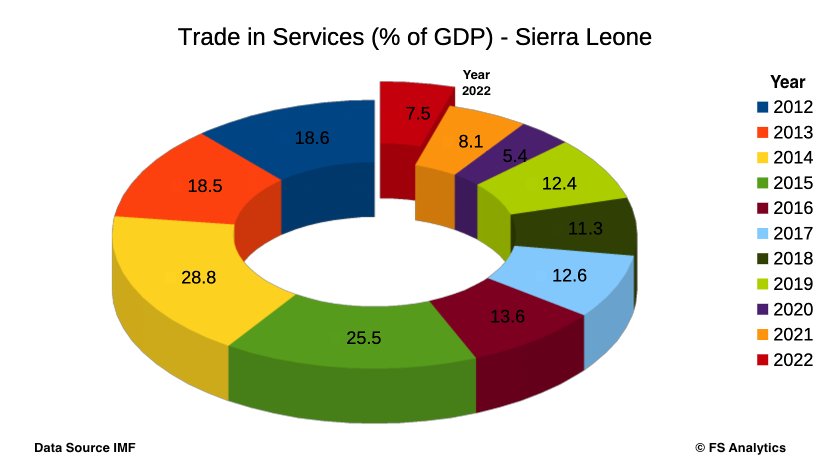
Trade in services, the sum of service exports and imports contribute immensely to the growth of country's Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Analytic Trends however have shown a decrease in this between 2021 and 2022. Trade in services accounted for approximately 7.5% of the Country’s GDP in 2022, a decrease of 0.6% from the 8.1% recorded in 2021. This drop suggests a contraction in a vital area that had previously shown promise by contributing to economic growth in a way that has diverted attention away from reliance on agriculture and mining. As global economies increasingly gravitate towards service-oriented frameworks, the performance of the country’s service sector encompasses a wide array of industries including tourism, banking, telecommunications, and education.
Recent data from International Monetary Fund (IMF) Balance of Payments Statistics Yearbook shows, that trade in 2022 in services was on an upward trajectory, reflecting a burgeoning sector that included tourism, telecommunications, and financial services. However, it was in 2014 that the service sector peaked at an impressive 28.8%, illustrating its potential as a cornerstone of national economic performance. This surge can be attributed to investments in infrastructure and a surge in attention on tourism and trade.
The winning streak of 2014 could not be sustained, as the percentage fell to 25.5% in 2015. A decline that marked the beginning of a downturn that has continued in subsequent years. The outbreak of the Ebola virus and the subsequent economic fallout had a crippling effect on travel, trade, and local businesses, leading to a drop to 13.6% in 2016 and further to 12.6% in 2017.In 2018, the situation deteriorated with trade in services hitting a low of 11.3%. The continued emphasis on agriculture as a primary sector sometimes overshadowed the service industry, which struggled to regain its footing. However, there was a slight recovery in 2019 to 12.4%, signalling cautious optimism as regional stability improved, and some recovery strategies were implemented.
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 marked a significant turning point for global economies, and Sierra Leone was no exception. The service industry was hit particularly hard, recording a staggering drop to just 5.4% of GDP. With borders closing, travel bans imposed, and local businesses heavily impacted, the country faced unprecedented challenges, necessitating immediate government intervention and reforms to support the sector.
Sierra Leone demonstrated resilience in the face of adversity, with trade in services rebounding to 8.1% in 2021 and slightly declining to 7.5% in 2022. While these figures still reflect the scars left by the pandemic, the recovery illustrates a gradual restoration of confidence. The efforts to diversify the economy, improve service delivery in key sectors like tourism and an enhanced telecommunications yield positive results.
Factors Contributing to the Decline
Several factors may have influenced this decline in service trade as a percentage of GDP:
- After effects of the Pandemic: The pandemic had a devastating impact on global tourism and related services. Despite recovery efforts, lingering effects such as travel restrictions and changes in consumer behaviour likely contributed to reduced service exports.
- Economic Challenges: Sierra Leone continues to grapple with various economic challenges, including high inflation rates, currency depreciation, and infrastructural deficits. These issues can erode investor confidence and hinder the growth of service-oriented businesses.
- Global Economic Environment: The broader global economic downturn, characterized by rising energy prices, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical uncertainties, also plays a role. These factors adversely affect Sierra Leone's export markets and demand for services. The decline in trade in services as a percentage of GDP raises several critical questions regarding the economic trajectory. A shrinking services sector may lead to reduced job creation, particularly for the youth population, which is heavily reliant on employment opportunities in this area.
Moreover, a sustained decrease in service trade could exacerbate challenges related to foreign exchange earnings, given that services such as tourism and remittances can significantly bolster the economy. If the trend persists, policymakers may need to implement strategic interventions to revitalize the sector.
Strategic Recommendations for Recovery
To address the decline in its service trade contribution, Sierra Leone could consider the following strategies:
- Promoting Tourism: Enhancing tourism infrastructure and marketing efforts to attract international visitors could be pivotal. Drafting targeted strategies to showcase cultural heritage, natural beauty, and unique experiences may boost revenues in this critical segment.
- Investment in Infrastructure: Improving telecommunications and transportation infrastructure would not only support existing services but also attract foreign investment, creating a more conducive environment for service-based businesses.
- Skill Development Programs: Enhancing education and vocational training in service-related fields can help equip the workforce with necessary skills, facilitating employment and entrepreneurship in burgeoning sectors like IT and hospitality.
- Diversifying Service Offerings: Encouraging local entrepreneurs to innovate and diversify the types of services offered can create new markets and opportunities for revenue generation.
The decrease in trade in services from 8.1% to 7.5% of GDP in 2022 signals a need for urgent attention from policymakers, industry leaders, and stakeholders. Strategies to bolster the services sector not only hold the potential to reverse this trend, but also to support broader economic stability and growth.
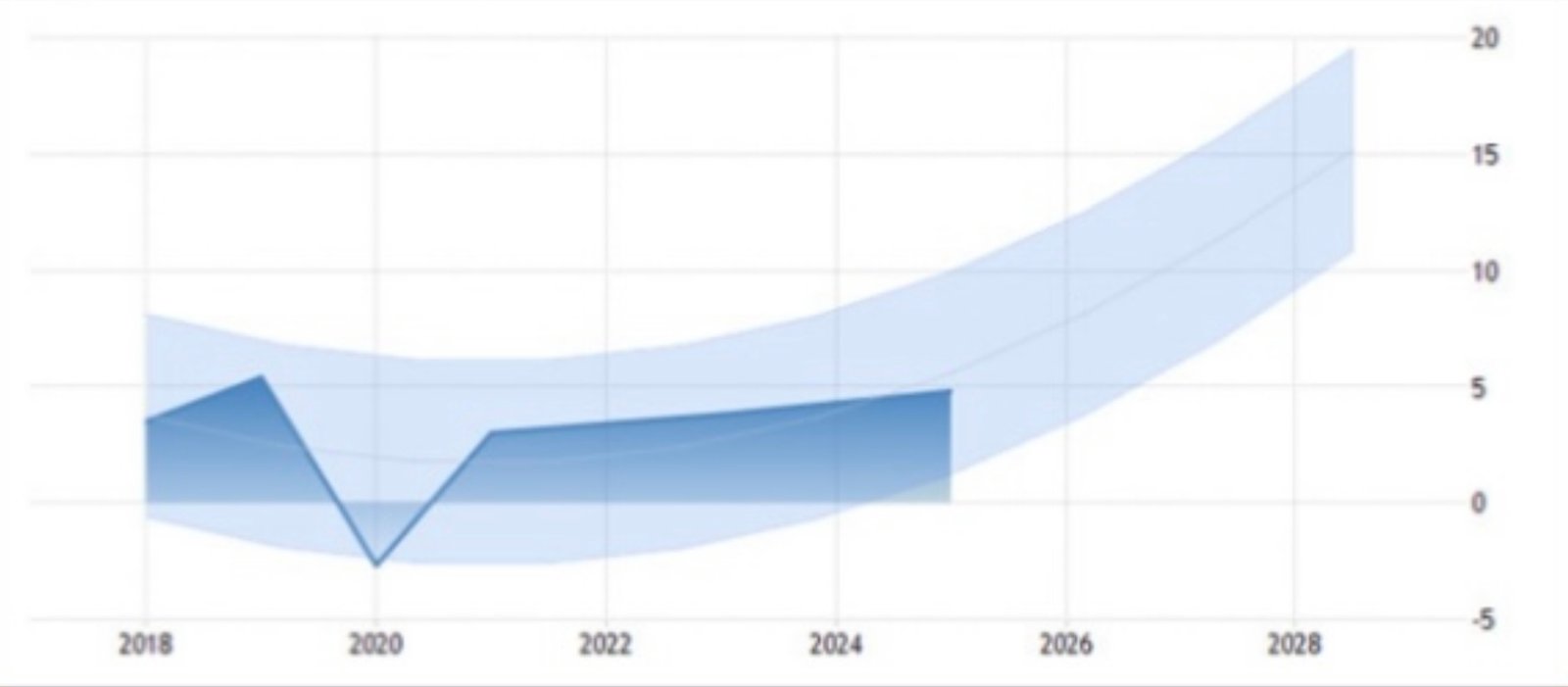
Looking forward, several factors could influence the trajectory of Sierra Leone's trade in services. Should the government continue to prioritize infrastructure development, increase access to digital services, and implement strategic marketing to attract foreign investment and tourism, this could expect an upward trend. Forecasts suggest that trade in services could rise modestly as the effects of the pandemic wane and global travel resumes.
The analytic trends in trade in services from 2012 present a picture of resilience and potentials. Moving ahead, a combination of strategic investments, improved governance, and a focus on innovation in the service sectors would unlock sustainable growth and ensures that it recovers in the coming years.
05-11-2024